News
How to Make Cotton Stalk into Fuel Pellets

I. Feasibility of Making Cotton Stalk Pellets
In the world, cotton accounts for nearly 40% of global fiber production. High cotton production is accompanied by generation of tons of cotton waste each year. Cotton stalk is the main biomass available in the field after the harvest of cotton, which are often disposed of by burning in the field.With the development of modern technology, cotton stalks can be turned into pellets by a wood pellet machine in stalk pellet production line. Making stalk pellets is the cost-effective investment due to competitive superiority of cotton stalk as biomass fuel and stalk pellet's own advantages in competition.
II. Abundant Raw Material
Approximately 80 countries worldwide produce cotton, the U.S., China, and India together provide over half the world’s cotton. Other major producers are Uzbekistan, Pakistan, Brazil, Turkey, Australia, Turkmenistan, Greece, Syria and Egypt.
US: Cotton production is an important economic factor in the United States as the country leads worldwide in cotton exportation. All most all the cotton fiber growth and production occurs in southern and western states. More than 99 percent of the cotton grown in the US is of the Upland variety. The final estimate of U.S. Cotton production in 2012 was 17.31 million bales.
India: It is estimated that about 25 million tons of cotton stalk is generated in India every year. Two leading cotton growing states in India are Gujarat and Maharashtra which together contribute over 50% of India’s cotton crop. Most of the stalk produced is treated as waste or it is used as fuel by rural masses. The bulk of stalk is burnt off in the field after the harvest of the cotton crop.
Uzbekistan: Due to its large agricultural sector, Uzbekistan has an enormous potential of biomass energy generation. Main source of biomass in the country is cotton stalk. The annual out of cotton stalk is about 3 million tons. Almost all of this cotton stalk resource is consumed for cooking and space heating in the rural area by using the most conservative combustion process.
Pakistan: Pakistan is an agricultural country and produces crop residues of about 84 million tons per year, out of 69 million tons are field based crop residues. Pakistan comes on the 4th position among the largest cotton producing countries in the world which produces 9.7 million bales per year contributing 8.81% of total world. The annual production of cotton stalks is around 13.20 million tons.
III. Cotton Stalk Properties
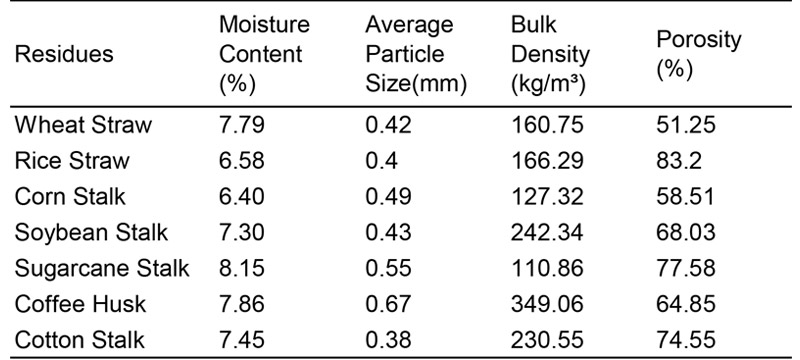
Depending upon the variety and the crop conditions, the stalks are 0.8 to 1.5 meters long and their diameter just above the ground may vary from 1 to 2.5 cm. The specific weight of short chopped stick is about 160kg/mآ³. The calorific value of cotton stalks is equivalent to poor quality wood. Heating value (or calorific value) is essentially a material for burning. Hence it is suitable raw material for making fuel pellets.A number of properties are commonly known to affect the success of pelleting, including: heating value, moisture content of the material, density of the material.
â—ڈ High Heating Value
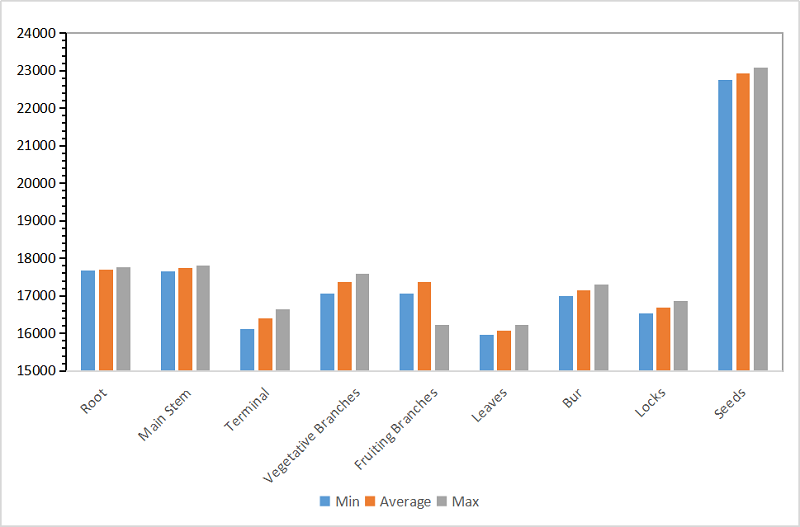
In terms of heating value, heating value ( or calorific value) is essentially a material for burning as fire or as a thermal source of energy. There is a calorific energy analysis in cotton plants could be helpful in developing highly applicable and productive planning for energy policies. The result shows that the calorific energy in different organs of cotton is different. The lowest calorific energy value in all plant organs was observed at leaves(15.955 KJ/g), while seeds contains the highest energy value varied between 22.750-23.078KJ/g. The calorific values of dry cotton stalks are varying from 15.861 to 15.100 KJ/g. Compared with other crop residues, the calorific energy of wheat straw, rice straw, corn stalk, soybean stalk are 17.98, 17.12-18.68, 15.40-18.25, 21.81-23.01 KJ//g, respectively. Therefore, cotton stalk can be used as pellet fuel in the respect of heating value.
â—ڈ Low Moisture Content of Cotton Stalk
Water is one of the most useful factor that are used both as a binder and lubricant. Therefore water is particularly necessary as an aid in pelletizing. Several investigations of different materials indicate that the strength and density of pellet increase with increasing moisture until an optimal level is reached. The optimal moisture content for agricultural residues to be pelletized ranges between 12-15%. Cotton stalk moisture content is in this range. The stalks are left on the field, thus losing about 80% of their moisture in about 5 days. That means the stalk moisture content reaches the recommended range in a time period of less than one week. This implies that cotton stalks can be pelletized one week after the harvest operation is finished without incurring any additional cost for drying.
â—ڈ High Bulk Density
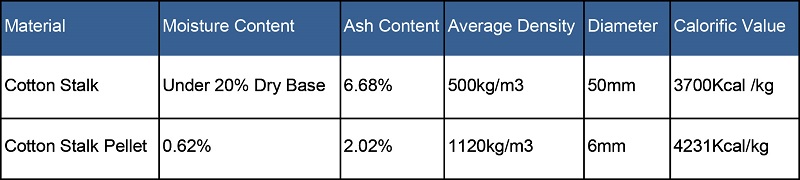
Bulk density is the ratio between the weight of the pellets and the amount of space they take up. It reflects the amount of solid material packed into the pellet and therefore has a relationship to the heat content of the fuel. Lower bulk density may result in lower conversion efficiency, as it gives rise to poor mixing characteristics and nonuniform temperature distribution, both of which may create unfavorable operating conditions in the thermochemical conversion systems. On the other hand,higher bulk density may result in lower transportation and storage costs and lower emissions during combustion. A good quality pellet will have a density of 650kg per mآ³. The pulverization of cotton stalk can increase its density to 1080kg per mآ³.
â—ڈ Comparison between Cotton Stalks and Cotton Stalk Pellets
IV. Processing Cotton Stalk Pellets
The cotton stalk pellet manufacturing process generally includes: crushing, drying, pelletizing,cooling and sieving and packaging.
â—ڈ Crushing: Before stalks can be pelletized, it is vital that the size of the material is suitable. The proper size is less than 6mm. Besides, cotton stalk is hard than normal agricultural straw. So the chaff cutter and hammer mill is necessary to crush stalk into short and fine particles.
â—ڈ Drying: Before stalks can be pelletized,it is vital that the moisture content of the material is suitable.The proper moisture content is about 12%-15%. If the material moisture is higher, rotary dryer is needed. But remember that raw materials should not be too dry, the minimal level is 12%.
â—ڈ Pelletizing: Stalk pellet making machine,also known as wood pellet machine, is available in different capacities. There are two types of fuel pellet machine, namely, vertical ring die wood pellet machine and flat die wood pellet machine. Vertical ring die wood pellet machine can be designed for 1-20t/h pellet line. The flat one is more suitable for small capacity or home use.
â—ڈ Cooling: As the pellets leave the pellet machine, they are hot and soft. Thus they need to be cooled in the pellet cooler. The cooling process is important for the strength and durability of the pellets.
â—ڈ Screening and Packaging: The cooled pellets should be passed over a vibrating screen to remove fines among the pellets. These fine materials can be sent back to the pelletizing process. Once screened, pellets areready to be packaged for the desired end use.
V. Application of Cotton Stalk Pellets
Cotton stalk pellet machine is developed according to the needs of the market. It is the equipment which takes corn straw, cotton straw, rice straw, sawdust, wood powder, peanut shells, rice husk and other agricultural wastes as raw materials to make them into pellet fuel. The finished particles after molding can be used in the fireplace, boiler, gasification furnace and biomass power generation factory. It also can be applied to the low-temperature granulation of biological fertilizer, organic fertilizer, compound fertilizer and so on.
VI.Benefits from Stalk Pellets
â—ڈ For government economy
For farmers, agricultural residues can turn into valued products. Traditionally after crop harvest, farmers burnt or otherwise disposed of stalks and other residues in the field.The marketability of drop stalks will boost local economies by providing jobs and services. An increase in farm earnings will diminish the need for farm subsidies, which will eventually reduce farmers’ reliance on the government for support. For industry, biomass pellets could replace the non-renewable furnace oil or natural gas, which can effectively reduce the production cost.
â—ڈ For environment
The burning of agricultural stalks causes air pollution, soil erosion, and a decrease in soil biological activity,which eventually leads to lower yields. However, burning yields smoke and other pollutants, which adversely effects air quality, visibility, and human and environmental health. Processing these stalks into pellets not only avoid environmental pollution but also make you get profit from the valued fuel pellets. These stalk pellets can be burned in heating furnaces, boilers, pellets stoves and traditional stoves, and other heating systems. The costs of granule heating are two-times lower than the costs of liquid fuel or liquefied gas.
VII. Prospect of Stalk Pellet Production
Abundant raw materials keep stalk pellet production sustainable
Global demand for cotton consumption continues to grow driven by the fiber demands of fast growing economics like India and China and the growing world population. It is estimated that, the global demand for cotton will be about 48 million metric tons by 2030. Broadly, there will be amount of cotton stalks as raw materials for pellet production line.
Development of bio-energy market provide opportunity for making pellets from stalks
Due to mounting social and political pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emission, bio-energy products are of increasing interest to developers and regulators. The combustion of biomass for energy is recognized as being neutral in terms of greenhouse gas emission. This will be great market for stalk pellet production.Therefore, it is time for embracing pellet making technologies for better transferring cotton stalk biomass into the valued form of bio-fuels.
Categories
News
Contact Us
Contact: Bolida
Phone: 86-0531-67880768
Tel: 86-0531-67880768
E-mail: sales@rotexmaster.cn
Add: Dazhan Village, Zaoyuan Street, Zhangqiu District, Jinan City, Shandong Province, China.